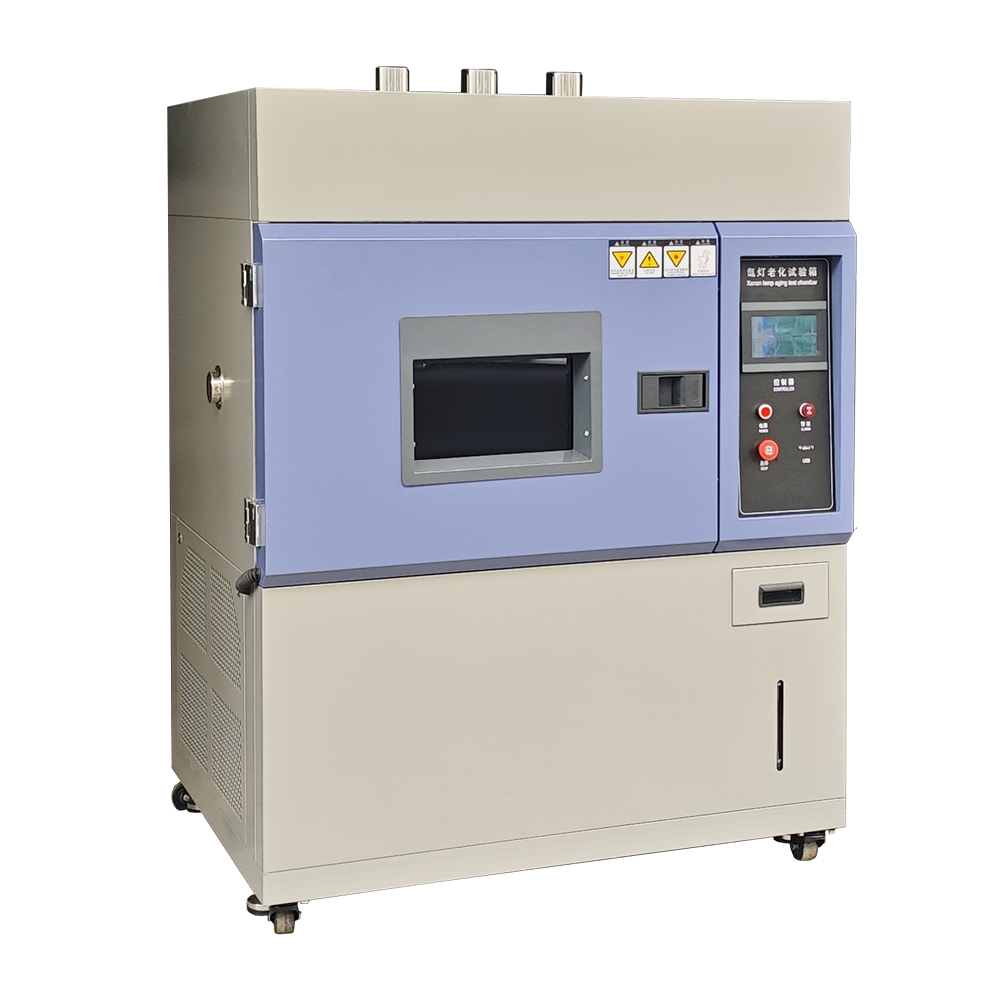

xenon test chamber factory
458005.0 INR/Unit
Product Details:
- Automation Grade Fully Automatic
- Accuracy 3%
- Interface Type RS232, USB
- Port Size DN50
- Measuring Range 0-1200 W/m (Irradiance)
- Equipment Type Xenon Test Chamber
- Features Programmable, Automatic Test Cycle, Overload Protection
- Click to view more
X
xenon test chamber factory Price And Quantity
- 458005.0 INR/Unit
- 1 Unit
- Double Layer with Observation Window
- Air Cooled Xenon Arc Lamp
- 1.8 kW
- SUS 304 Stainless Steel
- Leakage Circuit Breaker, Over-temperature Alarm
- Water Cooled / Air Cooling Optional
- Programmable Countdown Timer
- ASTM D2565, ISO 4892-2, GB/T 16422.2
- Rotary Carousel
xenon test chamber factory Product Specifications
- 100 Liters
- 0-1200 W/m (Irradiance)
- DN50
- RS232, USB
- 500 mm
- 3%
- Fully Automatic
- 450 mm
- Accelerated Weathering Simulation
- Adjustable, 42-120 min per cycle
- 24
- 0.1C (Temperature), 1% RH (Humidity)
- Programmable, Automatic Test Cycle, Overload Protection
- Xenon Test Chamber
- Programmable Touch Screen (PLC Control)
- Approx. 400 kg
- RT+10C to 70C
- 3s
- 30%-98% RH (Adjustable)
- Floor Stand
- 0-9999 hours
- 75 x 150 mm
- 220V/50Hz
- Material Aging Resistance Testing, Weather Resistance Test
- Digital LCD Touchscreen
- 1700 mm
- 0.5-0.7 MPa
- 50Hz
- AC 220V / 50Hz
- Double Layer with Observation Window
- Air Cooled Xenon Arc Lamp
- 1.8 kW
- SUS 304 Stainless Steel
- Leakage Circuit Breaker, Over-temperature Alarm
- Water Cooled / Air Cooling Optional
- Programmable Countdown Timer
- ASTM D2565, ISO 4892-2, GB/T 16422.2
- Rotary Carousel
xenon test chamber factory Trade Information
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- 90 Unit Per Month
- 7 Days
- All India
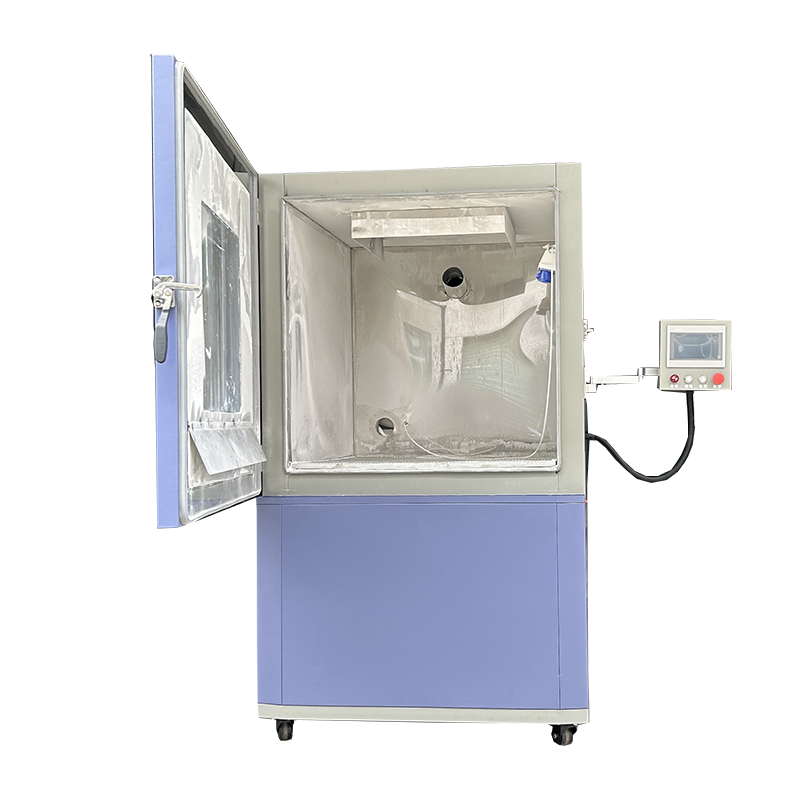
Product Description
Standard Features
| Model | DR-H301 |
| Internal dimension (WxDxH) | 500*600*500mm |
| External dimension (WxDxH) | 1000*1000*1750mm |
| Temperature range | RT+10~ 60 (suggest to use 402) |
| Temperature Fluctuation | 1 |
| Ozone concentration | 50~1000 pphm, adjustable |
| Ozone concentration deviation | 10% |
| Sample holder | SUS#304 stainless steel |
| Temperature controller | Programmable touch screen controller |
| Ozone concentration analysis | Concentration analysis meter |
| Ozone generator | High pressure silence discharge type |
| Protection system | Leakage, short circuit, over temperature, over heat |
| Test criteria | ASTM D1149, ISO 1431, JIS K6259... |
The core of the xenon lamp aging test chamber lies in its built-in xenon lamp tube, which plays a crucial role in simulating natural environments and accelerating material aging processes. The importance of xenon lamp aging test chamber tubes is as follows:
1. Spectral simulation
Xenon lamp tubes are capable of emitting light that closely resembles the solar spectrum, including ultraviolet (UV), visible light, and infrared (IR) wavelengths. This spectral simulation capability enables the xenon lamp aging test chamber to accurately reproduce the effect of sunlight on materials, thereby providing accurate test results.
2. High energy radiation
The radiation emitted by xenon lamps covers the entire visible spectrum and ultraviolet region, and has high brightness. This high-energy radiation can accelerate the aging process of materials, enabling the simulation of long-term natural aging effects in a short period of time, thereby shortening the testing cycle and improving testing efficiency.
3. Stability and consistency
The photoelectric parameters of xenon lamps have good consistency, and their working state is relatively less affected by changes in external conditions. This means that during the testing process, the xenon lamp can provide stable and consistent lighting conditions, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of the test results.
4. Wide range of applications
The lamp tube of the xenon lamp aging test chamber can simulate the lighting conditions under various environmental conditions, and is therefore widely used in multiple fields, including materials science, automotive industry, building coatings, plastic products, etc. For example, in the automotive industry, xenon lamp aging test chambers can simulate the long-term exposure of vehicle exterior components (such as bumpers and paint) to sunlight and rain, in order to evaluate their weather resistance.
5. Flexible lighting control
The lamp tube of the xenon lamp aging test chamber can adjust the light intensity and cycle to meet different testing needs. This enables the test chamber to simulate lighting conditions at different time periods, providing a more realistic aging simulation effect.
6. Cooling method
The working temperature of xenon lamps is very high and requires forced cooling, usually using air or water cooling methods. Different cooling methods can affect the service life and performance of the lamp tube. For example, water-cooled xenon lamps have higher luminous efficiency and longer lifespan.
7. Lifespan and Maintenance
The lifespan of xenon lamp tubes can usually reach 1600 hours. In daily use, regular replacement and maintenance of the lamp tube are important steps to ensure the normal operation of the test chamber. The operation of replacing the lamp tube is relatively simple, but it requires professional personnel to ensure safety and performance.
8. Security
The lamp tube of the xenon lamp aging test chamber generates high-energy radiation during use, so the equipment is usually equipped with multiple safety protection measures, such as over temperature protection, leakage protection, emergency stop button, etc. These measures ensure the safety of operators and the stable operation of equipment.
Water cooling and air cooling are two common cooling methods, each with its own characteristics in the application of xenon lamp aging test chambers. The following are the specific differences between water-cooled and air-cooled:
1. Cooling principle
Water cooling: The water cooling system uses circulating water to remove the heat generated by the xenon lamp tube. The water flows through the cooling sleeve or channel around the lamp tube, transferring heat to the cooling water, and then dissipating the heat to the environment through a radiator or cooling tower.
Air cooling: The air cooling system uses a fan to blow air through the lamp tube and radiator, taking away heat. Air, as a cooling medium, comes into direct contact with the lamp and radiator, taking away heat.
2. Cooling efficiency
Water cooling: The cooling efficiency of water cooling systems is usually higher than that of air cooling systems. Water has a high specific heat capacity, which enables it to absorb and transfer heat more effectively. Therefore, water cooling systems can maintain stable cooling effects under high power and load.
Air cooling: The cooling efficiency of air cooling systems is relatively low, especially under high power and high load conditions. The specific heat capacity of air is low, and its cooling capacity is limited, so air-cooled systems may not provide sufficient cooling effect under high loads.
3. Equipment complexity and maintenance
Water cooling:
Complexity: Water cooling systems are usually complex and require components such as water pumps, pipelines, radiators, cooling towers, etc. The increase in complexity and maintenance requirements of these components adds to the system.
Maintenance: The maintenance of the water cooling system is relatively frequent, and it is necessary to regularly check the quality of the cooling water, pipeline leaks, pump operation status, etc. In addition, the cooling water needs to be replaced regularly to prevent scaling and corrosion.
Air cooling:
Complexity: The air-cooled system is relatively simple, mainly composed of a fan and a radiator. Simple structure with low maintenance requirements.
Maintenance: The maintenance of the air-cooled system is relatively simple, mainly including regular cleaning of the fan and radiator to prevent dust and debris from affecting the cooling effect.
Comprehensive Weathering Simulation
Our xenon test chamber provides accelerated weathering simulation to evaluate the aging resistance of materials. Supporting a wide humidity range (30%-98% RH) and temperature control from RT+10C to 70C, it replicates real-world environmental conditions, enabling manufacturers to forecast product durability.
Advanced Control and Automation
Easily manage your testing procedures with a programmable PLC touchscreen, adjustable test cycles, and an automatic countdown timer. Users can monitor and record test data through RS232 and USB interfaces, ensuring traceability and ease of data management for quality assurance teams.
Built for Reliability and Safety
Crafted with an inner chamber of SUS 304 stainless steel and equipped with a rotary carousel specimen holder, it delivers high corrosion resistance and consistent specimen exposure. Safety features such as leakage circuit breaker, over-temperature alarms, and overload protection guarantee secure operation throughout testing cycles.
FAQ's of xenon test chamber factory:
Q: How does the xenon test chamber simulate accelerated aging and weather resistance?
A: The chamber uses an air-cooled xenon arc lamp (1.8 kW) to replicate the full sunlight spectrum, effectively simulating environmental conditions like UV, visible light, temperature, and humidity. Specimens are exposed on a rotating carousel, ensuring uniform light distribution for consistent accelerated aging and weather resistance results.Q: What standards does this xenon test chamber comply with, and why is compliance important?
A: This equipment meets ASTM D2565, ISO 4892-2, and GB/T 16422.2 standards. Compliance ensures your test results are globally recognized and valid for various regulatory and quality assurance purposes, which is essential for international trade and certification.Q: When should I use the programmable countdown timer feature during testing?
A: The programmable countdown timer is designed for precise test duration management. Use it to automatically start and stop testing based on your required cycle times (ranging from 42-120 minutes per cycle and up to 9999 hours total), ensuring accuracy and repeatability in accelerated weathering protocols.Q: Where is this xenon test chamber typically installed, and what is its mounting type?
A: This chamber is designed as a floor-standing unit and is commonly installed in quality control laboratories, research institutes, or industrial testing facilities concerned with evaluating material durability under simulated weather conditions.Q: What is the process for conducting tests using this chamber?
A: Simply load up to 24 specimens (75 x 150 mm each) onto the rotary carousel, set the desired test parameters (e.g., temperature, humidity, irradiance) via the digital LCD touchscreen, and start the test. The automation grade is fully automatic, allowing continuous, hands-off operation with programmable cycles and data logging.Q: How does the chamber ensure safe and reliable operation during testing?
A: Safety is reinforced by features such as a leakage circuit breaker, over-temperature alarm, and overload protection. The double-layer chamber door with observation window and SUS 304 stainless steel fabrication also contribute to safe, reliable, and long-lasting performance.Q: What are the benefits of using this xenon test chamber for material testing?
A: The main advantages include rapid, reproducible evaluation of material aging and weathering resistance, conformity to international standards, fully programmable and automatic test cycles, accurate digital monitoring, and robust safety measures, making it ideal for manufacturers, exporters, and suppliers seeking consistent, high-quality test outcomes.Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email







 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese